
一种概括了正常和二型糖尿病状态下的人类肝-胰岛轴的多类器官系统。
Introduction
思路:
- 二型糖尿病(Type 2 diabetes,T2DM)的流行已成为现代社会面临的最紧迫和最昂贵的医疗挑战之一。T2DM的特点是高血糖和胰岛素抵抗,通常伴随着胰岛β细胞功能障碍和肝脏的胰岛素抵抗。
- 在体内,葡萄糖平衡对于调节新陈代谢和满足个体的能量需求至关重要。肝脏和胰岛在维持血糖正常方面表现出双重功能。在空腹状态下,胰岛α细胞分泌胰高血糖素,诱导肝脏产生葡萄糖,为重要器官提供能量。餐后,胰岛β细胞分泌胰岛素,诱导肝脏摄取葡萄糖,促进葡萄糖分解。这些协调的器官间互动的失败可能导致血糖水平失调和代谢紊乱,如T2DM。
- 目前研究葡萄糖代谢和T2DM的努力很大程度上依赖于动物模型。然而:
- 由于物种差异,动物模型不能准确地代表人类生理,缺乏模拟人类代谢反应的能力。
- 研究不同组织之间的相互作用的体外培养仅限于细胞共培养,不能精确控制人体器官特异性特征并准确概括体内信号反馈回路。
- 类器官可以概括体内组织的关键结构和功能。芯片类器官系统能通过提供准确的生物力学线索、生化信号和器官-器官相互作用来控制组织微环境。
- 作者提出了一种微流体多类器官系统,用于研究人类肝-胰岛轴在正常和疾病环境中的胰岛素和葡萄糖调节。
Design and Operation of the Microfluidic Multi-Organoid System
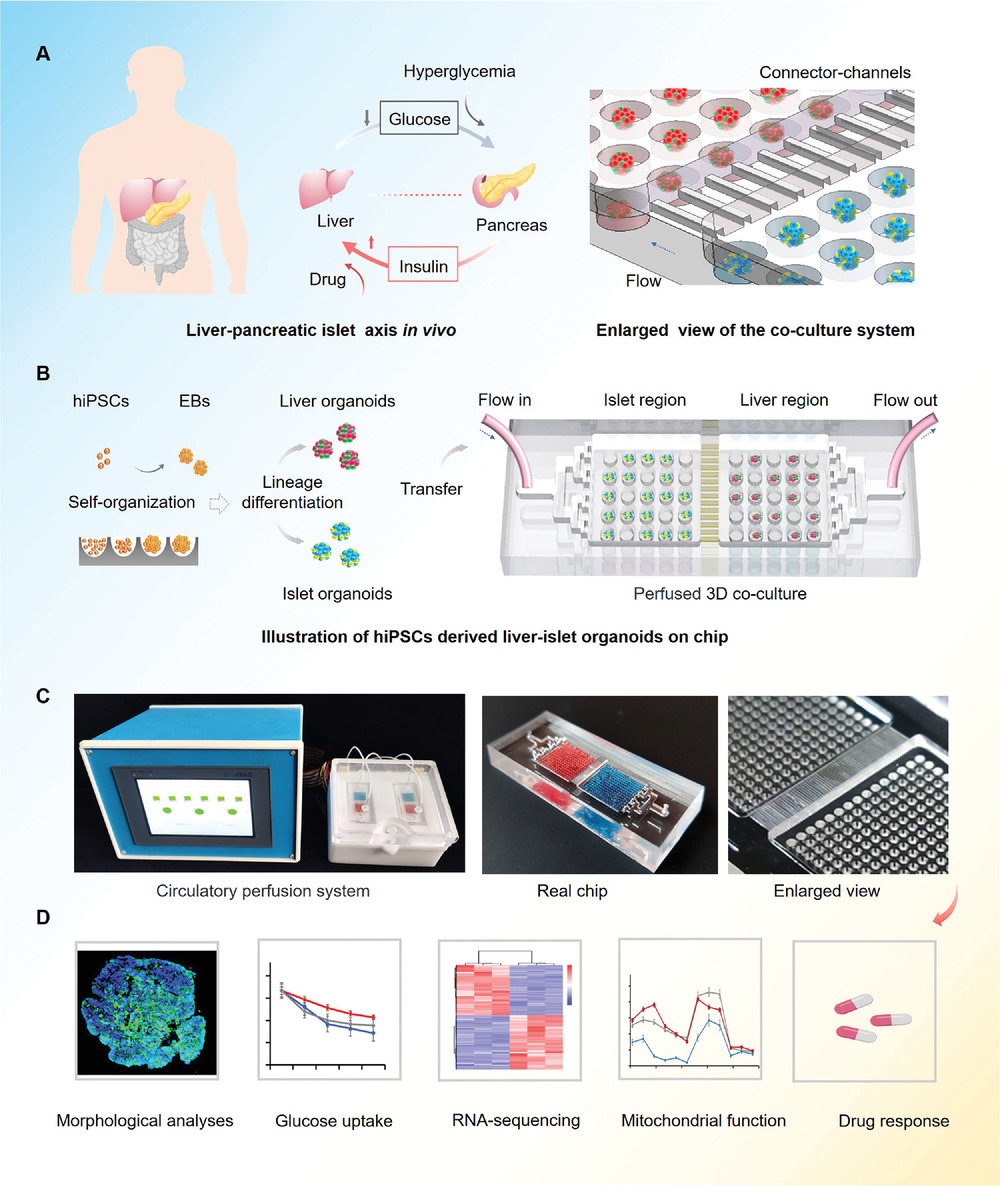
- (A)正常体内葡萄糖调节期间,人肝脏和胰岛组织之间相互作用的简化图示。即,胰岛β细胞分泌胰岛素促进肝葡萄糖摄取,从而将血糖水平维持在正常范围内。
- (B)在微孔阵列芯片中分化和生成hiPSCs衍生的肝脏和胰岛类器官的流程以及在多类器官芯片中的共培养实验装置。该设备由两个通过平行微通道网络连接的培养隔间组成,以支持两种类器官的共培养。人诱导多能干细胞(hiPSCs)在微孔阵列中自组织形成拟胚体(Embryoid bodies,EB),再分化成内胚层细胞(Endoderm cells,EC),最后分化成肝脏或胰腺类器官。
- (C) 微流控灌注系统和真实芯片。
- (D) 使用不同实验方法(形态分析、糖摄取、RNA测序、线粒体功能、药物反应)对肝-胰岛类器官系统进行功能分析。
Characterization of the hiPSC-Derived Liver and Pancreatic Islet Organoids

- (A)时间线以显示从hiPSCs到肝脏和胰岛类器官的分化过程。( DE,定形内胚层; HP,肝祖细胞; HC肝细胞; PE,胰腺内胚层; EP,内分泌祖细胞; EC,内分泌细胞。)
- (B)第20 d肝脏类器官中肝脏特异性蛋白的免疫组织化学染色,包括细胞色素P450(CYP3A4)、肝细胞标记物白蛋白(ALB) 和胆管细胞标记物细胞角蛋白7(CK7)。使用RT-PCR量化肝脏类器官中CYP3A4、ALB和CK7基因的相对mRNA表达水平。结果表明,hiPSCs衍生的肝脏类器官具有代谢药物的能力并含有天然肝脏的关键细胞成分。
- (C)通过免疫荧光染色测定第23 d胰岛类器官中β细胞胰岛素(INS)、α细胞胰高血糖素(GCG)、γ细胞胰多肽(PPY)和δ细胞生长抑素(SST)的胰腺谱系标志物的表达。使用RT-PCR量化胰岛类器官中INS、GCG、PPY和SST基因的相对mRNA表达水平。结果表明,本研究中产生的异质胰岛类器官包含四种经典的EC类型,使得它们类似于人类胰岛。
Improved Function of Co-Cultured Liver and Islet Organoids on a Chip

- (A-B)在延长培养期间的第5、15和30 d,用活/死试剂盒对肝脏和胰岛类器官进行染色。与单独培养相比,两种类器官的活性在共培养中更高。表明多类器官系统能促进类器官的生长和细胞活力。
- (C-D)在第1 d到第40 d的不同培养条件下检查肝脏类器官的白蛋白分泌和胰岛类器官的胰岛素分泌。结果表明,共培养能增强肝脏与胰岛的特异性功能。
- (E)定量单独培养的第1、15和共培养第15 d的肝脏特异性基因(CYP3A4、ALB和CK7)和胰岛特异性基因(NKX6.1、INS和GCG)的相对mRNA表达水平。表明,在适当时间(≈15 d),肝类器官功能基因的表达与胰岛类器官的功能基因的表达在共培养条件中得到增强。
- (F)在第15 d对肝脏类器官中的CYP3A4(红色)、ALB(红色)和CK7(绿色)和胰岛类器官中的NKX6.1(红色)、INS(红色)和GCG(绿色)进行免疫组织化学染色。总之,这种多类器官芯片系统可以在体外重现肝脏和胰岛之间的相互影响,并促进共培养类器官的生物功能,包括有效分化、良好的细胞活力和组织特异性功能。
NKX6.1:β细胞成熟相关转录因子
Transcriptional Analysis of Co-Cultured Liver and Islet Organoids

- (A-B)与单独培养相比,共培养中肝脏和胰岛类器官中显著差异表达基因(DEG)的火山图。以颜色标记以超过 2.0 倍数变化和 p<0.05 差异表达的基因。
- (C)单独和共培养的肝脏和胰岛类器官之间DEG的层次聚类热图。这种显著差异表明胰岛和肝脏类器官都受到共培养系统的影响。
- (D-E)第15 d在单独和共培养条件下肝脏和胰岛类器官DEG的KEGG富集分析。胰岛和肝脏类器官之间的相互作用增强了几种途径,包括肝脏类器官中的CYP450代谢、脂肪酸代谢和胰岛类器官中的代谢、糖酵解/糖异生和蛋白质消化和吸收相关的途径,这些途径对于维持肝脏稳态和葡萄糖刺激的胰岛素分泌(GSIS)非常重要。
- (F-G)使用qRT-PCR验证由RNA-seq鉴定的DEG。肝脏特异性基因(AFP、KRT19、PXR)、生长和代谢调节基因(IGF1)、脂质和葡萄糖代谢相关基因(PPRA、GCK、PCK1)和CYP450相关基因的转录(CYP1A2)显著上调。同样,与胰腺β细胞成熟(NKX2.2、HNF1B、NEUROD1)、胰腺外分泌细胞功能(AMY2B、PRSS2、KRT19)以及脂质和葡萄糖代谢(PEPCK、GCK)相关的基因在胰岛类器官中显著上调。
Crosstalk Between Liver and Islet Organoids on Chip
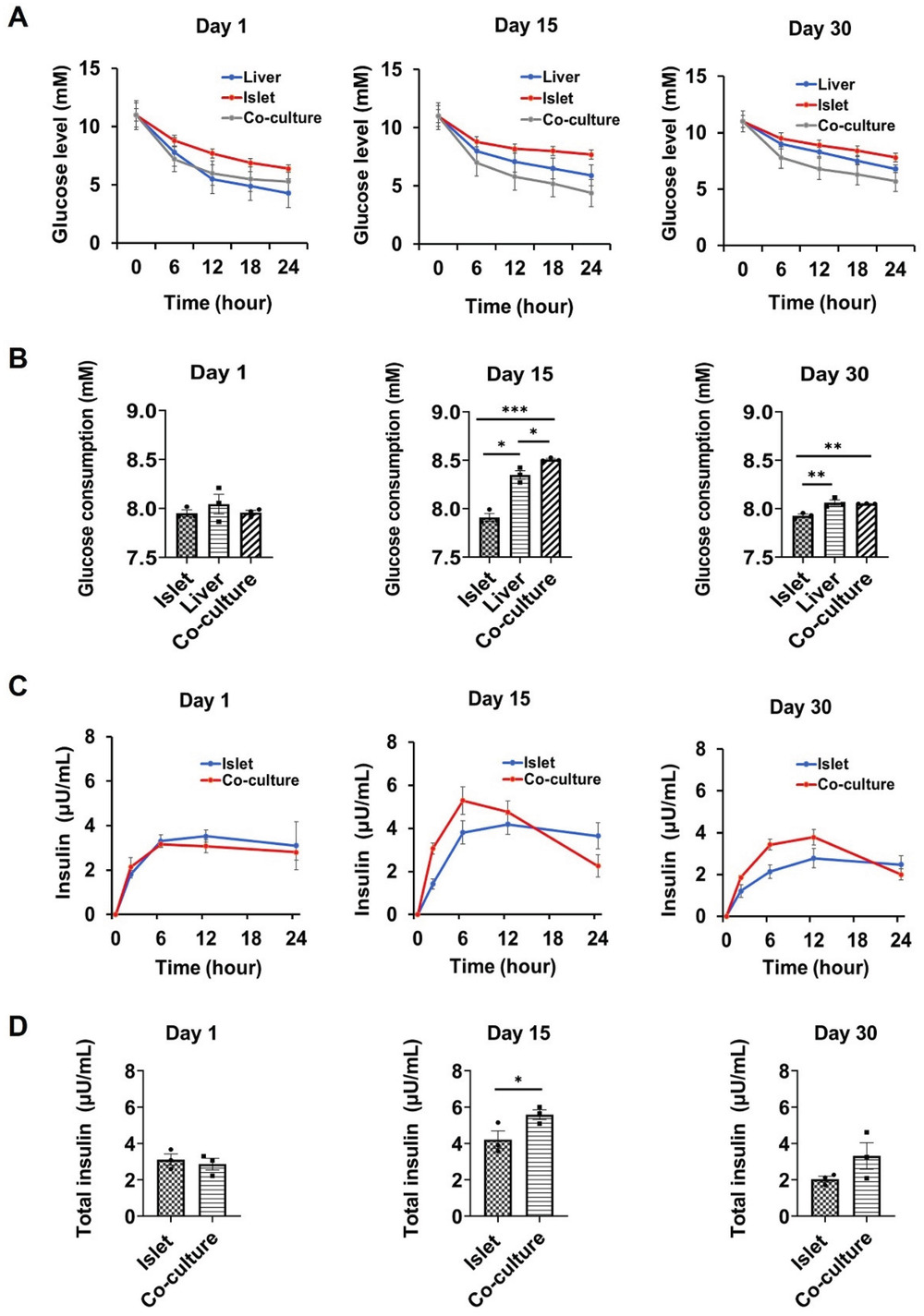
- (A)在单独培养和共培养的第1、15和30 d使用标准口服葡萄糖耐量试验(GTT)对动态葡萄糖水平进行量化。这里是将含有 11 mM葡萄糖的培养基注入单独或共培养系统,在不同时间点测量葡萄糖是否降到正常水平(3.9-6.1 mM)。
- (B)第1、15和30 d的葡萄糖消耗曲线下面积。与单独培养相比,第 15 d共培养系统中的葡萄糖消耗显著增加,表明肝-胰岛类器官芯片系统可以概括胰岛素刺激的葡萄糖摄取并维持体外生理性餐后血糖调节能力。
- (C)第1、15和30 d不同条件下GTT期间胰腺类器官的胰岛素分泌。结果表明,共培养的胰岛类器官对葡萄糖刺激敏感。
- (D)第1、15和30 d的胰岛素反应曲线下面积。显示共培养系统促进了胰岛类器官在高血糖条件下维持胰岛素分泌的能力。以上结果证实了建立的多类器官芯片系统可以有效地模拟胰腺β细胞衍生的胰岛素对葡萄糖的调节并刺激肝脏葡萄糖摄取。
Response of the Multi-Organoid System to Hyperglycemic Conditions
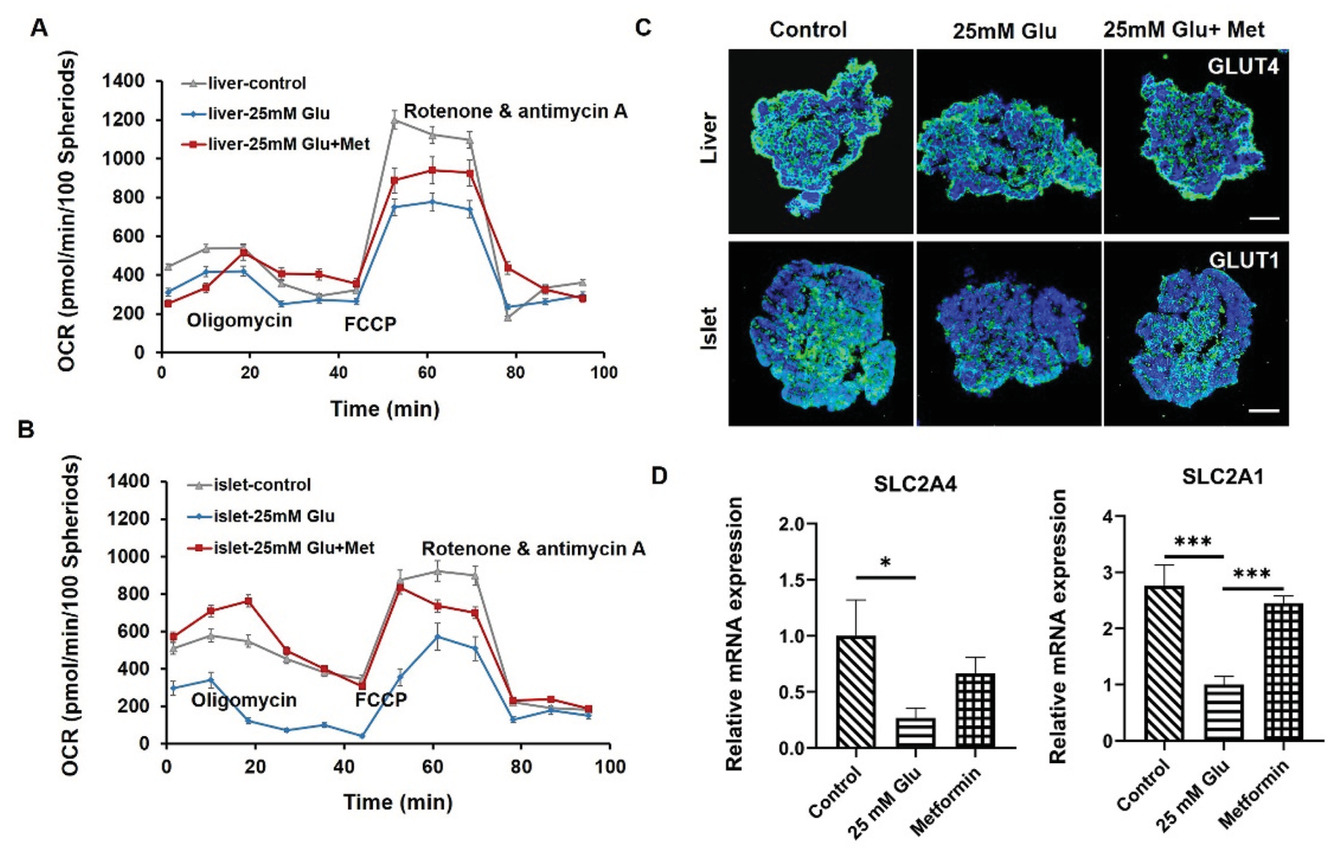
慢性高血糖是T2DM的主要原因,涉及多个代谢功能器官,包括肝脏和胰岛细胞。为了在高血糖环境中评估共培养的肝脏和胰岛类器官中的线粒体功能和葡萄糖转运蛋白表达,将多类器官芯片系统暴露于含有高浓度葡萄糖(25 mM)的培养基中5 d。通过量化细胞耗氧率(OCR)来评估线粒体功能。在实验期间的指定时间点添加寡霉素、FCCP和鱼藤酮/抗霉素A。
- (A-B)肝脏和胰岛类器官共培养15 d,然后暴露于三种培养条件(对照、25 mM葡萄糖和25 mM葡萄糖+100 mM二甲双胍)。 5 天后测量了这三种条件下肝脏和胰岛类器官的OCR。显示高血糖状态会削弱线粒体功能。而二甲双胍治疗后肝脏和胰岛类器官的呼吸能力和ATP生成得到改善,表明二甲双胍具有恢复线粒体功能的能力。
- (C)在第15 d不同处理条件下共培养的胰岛类器官中的葡萄糖转运蛋白标记GLUT1和肝脏类器官中的GLUT4的免疫荧光染色。
- (D)在第15 d使用RT-PCR对胰岛类器官中SLC2A1(编码 GLUT1)和肝脏类器官中SLC2A4(编码 GLUT4)的相对mRNA表达水平进行定量分析。表明在高血糖环境中,肝脏和胰岛类器官中葡萄糖转运蛋白的表达水平降低,模拟了糖尿病早期已知的病理过程。且证实了二甲双胍治疗后,葡萄糖转运功能的恢复。
Discussion
- 提出了一种源自hiPSC的多类器官芯片系统,用于在体外模拟肝-胰岛轴,并研究正常和2型糖尿病中肝和胰岛之间的相互作用。
- 该系统中的替代功能GTT测定表明,葡萄糖调节中的肝-胰岛相互作用主要涉及胰岛类器官的胰岛素分泌和肝类器官对葡萄糖的摄取。胰岛类器官响应葡萄糖分泌胰岛素并促进共培养系统中肝葡萄糖的摄取。
- 高血糖是糖尿病发展的主要因素,导致患者许多器官出现全身性病理变化。为了模拟胰岛和肝细胞中葡萄糖诱导的病理变化,将胰岛-肝类器官系统暴露于高葡萄糖培养基中。然后通过直接量化类器官中的线粒体呼吸来评估线粒体功能并观察到细胞 OCR 降低。这些结果与先前的报道一致,即高血糖和T2DM可诱导线粒体功能障碍、ROS产生、氧化应激和组织损伤。
Reference
Tao T, Deng P, Wang Y, et al. Microengineered Multi-Organoid System from hiPSCs to Recapitulate Human Liver-Islet Axis in Normal and Type 2 Diabetes[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(5): 2103495.



